Impact of Dormancy-Modulating Chemical Treatments on Seed Storage Stability and Protein Profiling in Mungbean (Vigna radiata L.)
Main Article Content
Abstract
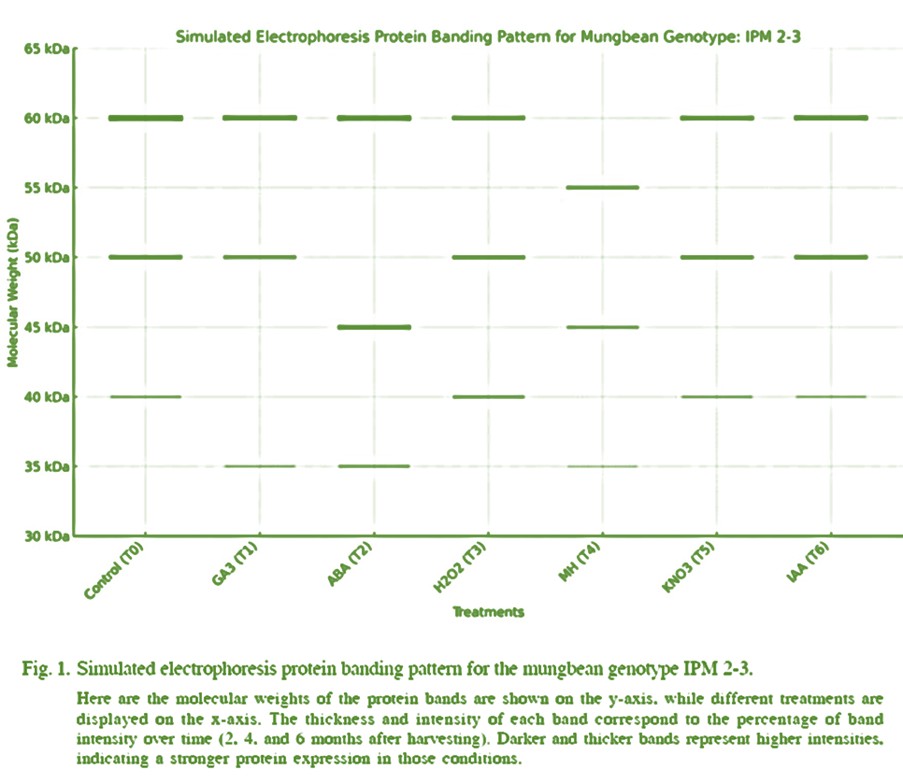
This study evaluates the effects of different dormancy-modulating chemical treatments on seed storability, physiological stability, and protein profile integrity in mungbean (Vigna radiata L.) genotype IPM 2-3. Treatments included gibberellic acid (GA3, 80 ppm), abscisic acid (ABA, 50 ppm), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2, 10 mM), maleic hydrazide (MH, 1000 ppm), potassium nitrate (KNO3, 1 mM), indole-3-acetic acid (IAA, 100 ppm), and an untreated control. Seed viability and electrical conductivity (EC) were assessed at two-, four-, and six-months post-harvest to examine long-term impacts on membrane integrity and physiological health. The untreated control (T0) maintained the highest viability (82.33% at two months, decreasing to 62.67% at six months) with the lowest EC values (0.213 dS/m/gm at two months, decreasing to 0.073 dS/m/gm at six months). Among treated seeds, GA3 sustained high viability (79.33% initially, 59% at six months) and moderate EC values, suggesting enhanced storability. In contrast, MH treatment showed the lowest viability (42% at six months) and highest EC (0.303 dS/m/gm initially), indicating significant membrane degradation and compromised physiological health. SDS-PAGE protein profiling revealed that T0, GA3, and ABA treatments had strong protein bands at 60 kDa and 50 kDa, correlating with high viability and lower EC, whereas MH-treated seeds showed weak bands at 55 kDa and 45 kDa, indicating substantial protein degradation. Statistical analysis confirmed a negative correlation between seed viability and EC, and a positive correlation between viability and protein band intensity. Overall, GA3 and ABA treatments support balanced dormancy modulation and storability, while MH adversely affects seed quality, providing valuable insights for optimizing mungbean seed storage practices.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.