Sustainable Ways of Zinc Management to Improve Growth and Metabolic Constituents in Wheat
Main Article Content
Abstract
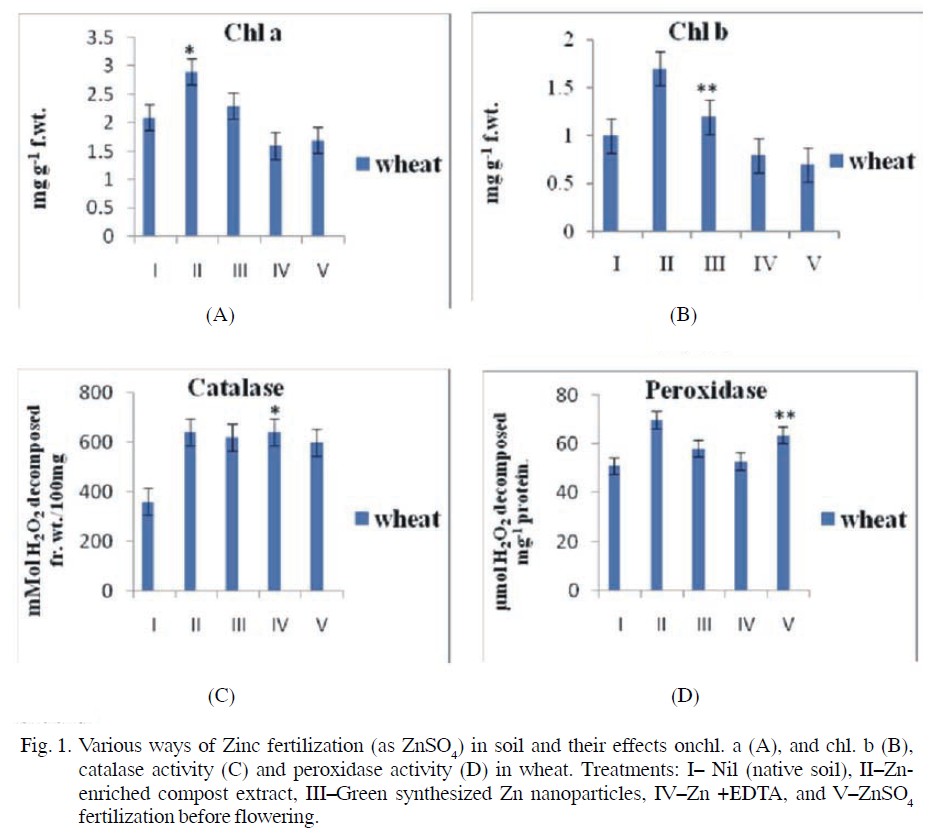
The effect of various ways of sustainable zinc management in soil to improve the growth of plants (length and dry weight), some biochemical parameters (pigments and protein contents, and the activity of catalase and peroxidase) in wheat was studied.A clay pot experiment was conducted.
The amendment of zinc was made as I- nil (control), II- Zn-enriched compost extract (40%), III- Green synthesized Zn nanoparticles, IV- Zn + EDTA, and V- ZnSO4 fertilized in the soil to find out the best sustainable way of Zn fertilization. The experiment was conducted in triplicates. Maximum dry weight (+50%), pigments, and protein contents (+36.8%) were found when Zn-enriched compost extract (40%) was applied to the soil. A single application of ZnSO4 also increased all the determined parameters in wheat, but the effect was less than the Zn-enriched compost extract. Among all treatments, Zn-EDTA showed the least promotery effects on wheat vegetative growth, but the effect was maximum at reproductive yield (length and weight of inflorescence and grains weight).
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.