Tetratrophic Associations of Hyperparasitoids of Aphids (Aphididae: Hemiptera) and their Distribution in India
Main Article Content
Abstract
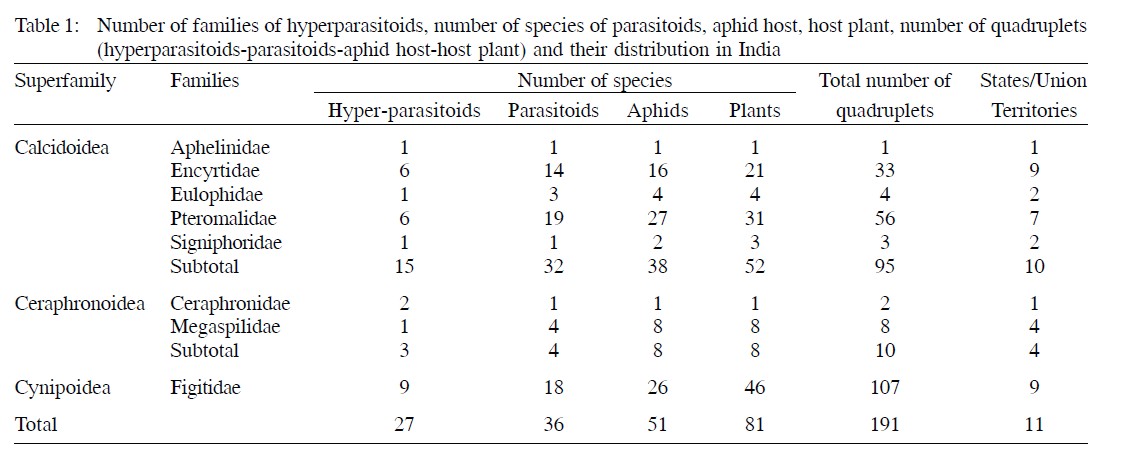
Aphid hyperparasitoids are secondary parasitoids constituting fourth trophic level which develop on primary parasitoids of aphids. Based on oviposition and feeding behaviour, they may be endophagous (develop in the larvae of primary parasitoids) or ectophagous (feed externally on the larvae of primary parasitoids when aphids are killed or mummified). Hyperparasitism has traditionally been considered harmful to the parasitoids and hence is excluded in biological control programmes. Their detailed biology and ecology are less known than their primary parasitoids. The present article provides a tetratrophic association of aphid hyperparasitoids of India. A total of 27 species of aphid hyperparasitoids belonging to 3 superfamilies of Hymenoptera are recorded in 11 states/union territories of India. These hyperparasitoids parasitise 36 species of primary parasitoids parasitising 51 species of aphids infesting 81 species of food plants. The Calcidoidea is the largest superfamily and comprises 15 species of aphid hyperparasitoids belonging to 5 families followed by Cynipoidea (9 species of aphid hyperparasitoids belonging to a single family) and Ceraphronoidea (3 species of aphid hyperparasitoids in two families). Among them, Alloxysta spp. are highly polyphagous and hyperparasitise 16 species of parasitoids that parasitise 26 species of aphids on 45 food plants in 9 states/union territories of India followed by Syrphophagus (14 species of parasitoids that parasitise 14 species of aphids on 17 food plants in 9 states/union territories), Pachyneuron (12 species of parasitoids that parasitise 16 species of aphids on 17 food plants in 4 states/union territories), Asaphes (8 species of parasitoids that parasitise 16 species of aphids on 17 food plants in 4 states/union territories). Binodoxys indicus (Subba Rao & Sharma), parasitising 7 species of aphids infesting 28 species of host plants was observed to serve as host for 14 species of hyperparasitoids while Lipolexis oregmae parasitises 9 species of aphids infesting 17 species of host plants serving as host for 6 species of hyperparasitoids. Indeed, no investigation was conducted in most of the states and union territories of India regarding the tetratrophic associations of aphid hyperparasitoids and hence, it requires an extensive survey in these areas to record them particularly in the agroecosystems to establish their relationship with aphid hosts and their parasitoids on different crops.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
Ahmad, M.J. & Ahmad, S.B. (2013). Dynamics of Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) (Braconidae: Aphidiidae) and its hyperparasitoid on mustard aphid, Lipaphis erysimi Kalt infesting brown mustard, Brassica campestris Linn. in Kashmir, India. J. Biol. Cont., 27(4): 247-252.
Ahmad, M.E. & Kumar, K.M. (2007). Food plants and natural enemies of Aphis craccivora Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae) in northeast Bihar. J. Aphidol., 21: 97-102.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1991). New host association of alloxystid hyperparasitoid. Newsl., Aphidol. Soc., India, 9(2): 8-10.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1992). New host association of chalcidoid hyperparasitoids. J. Adv. Zool., 13: 66-67.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1994). Aphis gossypii Glover on different food plants and its association with parasitoids and hyperparasitoids in Northeastern Uttar Pradesh. Ann. Entomol., 12: 63-67.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1995a). Records of Macrosiphini of north eastern Uttar Pradesh and its relationship with food plants and natural enemies. J. Aphidol., 9: 80-86.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1995b). Survey of parasitoids of aphids in north-eastern Uttar Pradesh for possible use in biological control. Ann. Entomol., 13: 87-96.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1996a). Trophic relations of aphid hyperparasitoids in north-eastern Uttar Pradesh. Entomon, 21: 37-42.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1996b). Tetratrophic interaction of Aphis craccivora Koch in Northeastern Uttar Pradesh. IPM & Sustainable Agriculture - an Appraisal, 6: 143-146.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (1997). Records of aphids and their food plants, parasitoids and hyperparasitoids from north Bihar. J. Adv. Zool., 18(1): 54-61.
Ahmad, M.E. & Singh, R. (2005). Food plants associations, seasonal occurrence and parasitoids/hyperparasitoids of few species of Aphis Linnaeus from northeastern Uttar Pradesh and Bihar. J. Adv. Zool., 26: 41-46.
Ahmad, M.E., Kumar, K.M., Parween, N. & Kumar, S. (2009). Tetratrophic associations of Aphis gossypii Glover with its food plants and natural enemies in northeast Bihar. In: Ecofriendly Insect Pest Management (Ed. Ignacimaithu, S. & David, B.V.), Elite Publication House, pp. 144-152.
Ahmad, M.E., Kumar, S., Parween N. & Rakhshan (2020). Bio-ecological study of few species of Aphis Linn. in northeast Bihar and their association with food plants and natural enemies for possible use in the biological control. J. Adv. Zool., 41(1&2): 103-116.
Bhagat, R.C. (1982). Aphid-galls and their parasitoids from Kashmir, India. Entomon, 7: 103-105.
Bhagat, R.C. (1983). Records and host range of hyperparasitoids (Insecta: Hymenoptera) of aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) from Kashmir, India. Sci. & Cult., 49: 150-152.
Bhagat, R.C. (1984). New records and hosts of aphid parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) from Kashmir, India. J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc., 81(1): 91-98.
Bhagat, R.C. (1987). Field Observations on hyperparasites of aphid pests infesting Rosa spp. in Kashmir valley, India. J. Biol. Cont., 1(2): 104-105.
Bijoy, C. & Rajmohana, K. (2013) Descriptions of four new species of the genus Alloxysta Förster (Hymenoptera: Cynipoidea: Figitidae: Charipinae) from India. Biosystematica, 7(1): 59-66.
Chakrabarti, S. & Debnath, M. (2009). Diversity of aphidophagous parasitoids (Insecta) of northwest and western Himalayas, India. In: Biodiversitat und Naturausstattung im Himalaya, III (eds. Hartmann, M.& Weipert, J.), Naturkundemuseum Erfurt, pp. 441-454.
Cusumano, A., Harvey, J.A., Bourne, M.E., Poelmana, E.H. & de Boerb, J.G. (2020). Exploiting chemical ecology to manage hyperparasitoids in biological control of arthropod pests. Pest Manag. Sci., 76: 432-443.
Das, B.C. & Chakrabarti, S. (1989). Praon himalayensis, a new walnut aphid parasitoid (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) in Garhwal range of Western Himalaya. Entomon, 14: 345-347.
Das, B.C. & Chakrabarti, S. (1990). New and little known aphidiid parasitoids (Hymenoptera; Aphidiidae) of gall forming aphids in Western Himalaya, with notes on their seasonal history. Orient. Ins., 24: 399-414.
Das, B.C. & Chakrabarti, C. (2018). Diversity and distribution of hyperparasitoids of Aphidiinae (Insecta: Braconidae: Hymenoptera) in the Garhwal Himalayas. Hartmann, Barclay. & Weipert: Biodiversität und Naturausstattung im Himalaya VI. - Erfurt, pp. 565-570.
Dharmadhikari, P.R. & Ramaseshiah, G. (1970). Recent records of aphidiids (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) in India. Tech. Bull. Commonw. Inst. Biol. Cont., 13: 83-89.
Favret, C. (2024). Aphid Species File: https://Aphid.SpeciesFile.org, retrieved on October 31, 2024.
Ferrer-Suay, M., Selfa, J. & Pujade-Villar, J. (2013). Charipinae fauna (Hymenoptera: Figitidae) from Asia, with description of eleven new species. Zool. Stud. 52(41): 1-26.
Fiske. W.E. (1910). Superparastism: an important factor in the natural control of insects. J. Econ. Entomol., 3: 88-97.
Frazer, B.D. & van den Bosch, R. (1973). Biological control of the walnut aphid in California: the interrelationship of the aphid and its parasite. Environ. Entomol., 2(4): 561-568
GBIF (2024). The Global Biodiversity Information Facility, retrieved on October 31, 2024, https://www.gbif.org
Godfray, H.C.J. (1994). Parasitoids: Behavioral and Evolutionary Ecology. Princeton, NJ: Princeton Univ. Press, pp. 473.
Gutierrez, A.P. & van den Bosch, R. (1970). Studies on the host selection and host specifity of the aphid hyperparasite Charips victrix (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae). 2. The bionomics of Charips victrix. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Amer., 63:1355-1360.
Hassell, M. P. & Waage, J. K. (1984). Host-parasitoid population interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 29: 89-114.
Heraty, J. & Woolley, J. (2024). Chalcidoidea of the World. CABI Publication, pp. 480.
Holler, C., Micha, S.G., Schulz, S., Francke, W. & Pickett, J.A. (1994). Enemy-induced dispersal in a parasitic wasp. Experientia, 50: 182-185.
Kumar, K.M. (2012). Species of genus Toxoptera Koch (Homoptera: Aphididae) in northeast Bihar. J. Aphidol., 25 & 26: 31-38.
Kumar, K.S. (2013). Seasonal abundance of Myzus persicae (Sulzer) and its association with food plants and natural enemies in Northeast Bihar. Biolife, 1: 195-194.
Luck, R.F. Messenger, P.S. & Barbieri, J.F. (1981). The influence of hyperparasitism on the performance of biological control agents, pp. 34-42. In. The role of hyperparasitism in biological control: a symposium (ed. Rosen, D.). Division of Agricultural Sciences, University of California, Berkeley, CA.
Matejko, I. & Sullivan, D.J. (1984). Interspecific tertiary parasitoidism between two aphid hyperparasitoids: Dendrocerus carpenteri and Alloxysta megourae (Hymenoptera: Megaspilidae and Cynipidae). J. Wash. Acad. Sci., 74: 31-38.
Miko, I., Yoder, M.J. & A.R. Deans (2011). Order. Hymenoptera, Family Megaspilidae, Genus Dendrocerus. Arthropod families of the UAE, 4: 353-374.
Nagalingam, B. (1988). Studies on the ecology and biocontrol agents of Myzus persicae (Sulzer). Newsl. Aphidol. Soc. India, 7 (1): 14-15.
Pandey, K.P., Kumar, A., Shanker, S. & Tripathi, C.P.M. (1985). First record of Pachyneuron aphidis (Bouche) (Pteromalidae: Hymenoptera), a hyperparasitoid of Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) (Aphidiidae: Hymenoptera) from India. Curr. Sci., 54: 710.
Poddar, S.C. (1982). Studies on Aphis craccivora Koch and its natural enemies in some parts of India. Ph.D. thesis, Calcutta University, Kolkata, West Bengal, pp. 245. http://hdl.handle.net/10603/162498
Poelman, E.H., Cusumano, A. & de Boer, J.G. (2022). The ecology of hyperparasitoids. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 67: 143-161.
Rao, V.P., Dharmadhikari, P.R., Ramaseshiah, G., Phalak, V.R. & Madhavan, T.V.S. (1969). Study of natural enemies of aphids (for the U.S.A.). Rep. Commonw. Inst. Biol. Cont., 1968: 45-47.
Sarkar, S. (2022). Incidence and host association of primary parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Braconidae: Aphidiinae) of aphids infesting economically important plants in Kumaon-Garhwal ranges of western Himalaya. Internat. J. Agric. Innov. & Res., 10(4): 137-142.
Sethumadhavan, T.V. & Dharmadhikari, P.R. (1969). Notes on Diaeretiella rapae (M’Intosh) (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) parasitic on aphids on crucifers in India. Tech. Bull., Commonw. Inst. Biol. Cont., 11: 173-177.
Singh, R. & Sinha, (1979). First record of Alloxysta sp., a hyperparasitoid of Trioxys (Binodoxys) indicus Subba Rao and Sharma (Aphidiidae: Hymenoptera). Curr. Sci., 48: 1008-1009.
Singh, R. & Tripathi, R.N. (1987). First record of hyperparasitism in two species of aphid parasitoid by Alloxysta pleuralis (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Alloxystidae). Newsl. Aphidol. Soc., India, 6(1): 11-12.
Singh, R. & Tripathi, R.N. (1988a). New host associations of the parasitoid and hyperparasitoid of aphids from India. Newsl. Aphidol. Soc. India, 7(2): 6-8.
Singh, R. & Tripathi, R.N. (1988b). New host associations of Alloxysta pleuralis (Cameron) (Hymenoptera: Alloxystidae). Newsl. Aphidol. Soc. India, 7(1): 11-12.
Singh, R. & Tripathi, R.N. (1988c). New host records of the parasitoid Lysiphlebus delhiensis (Subba Rao & Sharma) and the hyperparasitoid Alloxysta pleuralis (Cameron). Curr. Sci., 57: 397.
Singh, R. & Tripathi, R.N. (1991). Records of aphid hyperparasitoids in India. Bioved, 1(2); 141-150.
Singh, R., Pandey, R.K., Kumar, A. & Sinha, T.B. (1982). First record of three hyperparasitoids of Trioxys (Binodoxys) Indicus Subba Rao Sharma (Hym: Aphidiidae) from India. Entomon, 8(3): 329-330.
Singh, R., Srivastava, M. & Srivastava, P.N. (1987). New aphidiid host record of aphid hyperparasitoid Hymenoptera) form India. Entomon, 12: 115-116.
Singh, R., Upadhyaya, B.S., Singh, D. & Chaudhary, H.C. (1999). Aphids (Homoptera: Aphididae) and their parasitoids in north-eastern Uttar Pradesh. J. Aphidol., 13: 49-62.
Sullivan, D.J. & Völkl, W. (1999). Hyperparasitism: multitrophic ecology and behavior. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 44: 291-315.
Sullivan, D.J. (1987). Insect hyperparasitism. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 32:49-70
Thakur, J.N., Rawat, U.S., Pawar, A.D. & Sidhu, S.S. (1989). Natural enemy complex of the cabbage aphid Brevicoryne brassicae L. (Homoptera: Aphididae) in Kullu Valley, Himachal Pradesh. J. Biol. Cont., 3(1): 69.
Trivedi, T.P. & Rajagopal, D. (1988). Natural enemies of potato aphids, Myzus persicae (Sulzer) and Aphis gossypii Glover (Homoptera: Aphididae) in India. Biocovas, 1: 173-177.
Viggiani, G. (1984). Bionomics of the Aphelinidae. Annu. Rev. Entomol., 29: 257-276.
WFO (2024). The World Flora Online, https://www.worldfloraonline.org, retrieved on October 31, 2024.